Skip the Supplements: Drink This Golden Milk to Keep Cancer at Bay
Turmeric, the golden spice often found in curry, is far more than a kitchen staple—it’s a powerful cancer-fighting ally. For centuries, turmeric has been central to traditional Chinese, Islamic, and Ayurvedic healing practices. Modern research now supports what ancient wisdom has long known: turmeric, especially its active compound curcumin, offers serious protection against cancer.
Curcumin is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent that protects cells from damage and slows the growth of cancer cells. According to a 2024 review in Frontiers in Nutrition, curcumin works by disrupting the pathways cancer cells use to grow uncontrollably, triggering their natural death process and cutting off blood supply to tumors. It also neutralizes free radicals—unstable molecules that damage DNA and can trigger cancerous mutations.
But curcumin isn’t acting alone. Turmeric contains over 200 other compounds, including DMC and BDMC, which may be even more effective at preventing cancer from spreading. Turmeric also boosts the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiation while helping to reduce side effects like fatigue, pain, and dry mouth. It can even help break down cancer’s resistance to certain drugs.
While turmeric supplements are popular, experts caution against them. High concentrations in pill form can interact with medications like warfarin or reduce the effectiveness of pain relievers. Johns Hopkins Medicine recommends skipping the pills and using fresh turmeric instead.
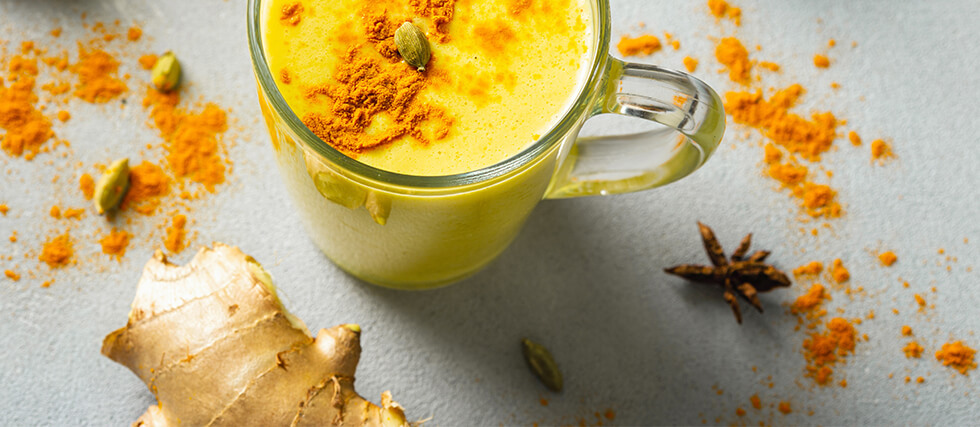
One of the most delicious and health-boosting ways to enjoy turmeric daily is by drinking golden milk. This warm, soothing drink combines turmeric with black pepper (to enhance absorption), ginger, cinnamon, and your choice of milk. Not only is it comforting and tasty, but it’s a simple, natural way to help your body stay resilient. When it comes to cancer prevention, golden milk may be the best daily habit you haven’t tried yet.
Golden Milk Recipe (Turmeric Milk)
Ingredients:
- 1 cup full fat coconut milk
- 1 teaspoon ground turmeric (or 1-inch piece of fresh turmeric, grated)
- ½ teaspoon ground cinnamon
- ¼ teaspoon ground ginger (or a small slice of fresh ginger)
- Pinch of black pepper
- 1 teaspoon honey or maple syrup
Instructions:
- In a small saucepan, add all the ingredients.
- Whisk together over medium heat until the mixture is hot but not boiling.
- Reduce the heat and simmer for 5–10 minutes, stirring occasionally.
- Strain (if using fresh turmeric or ginger), pour into a mug, and enjoy warm.